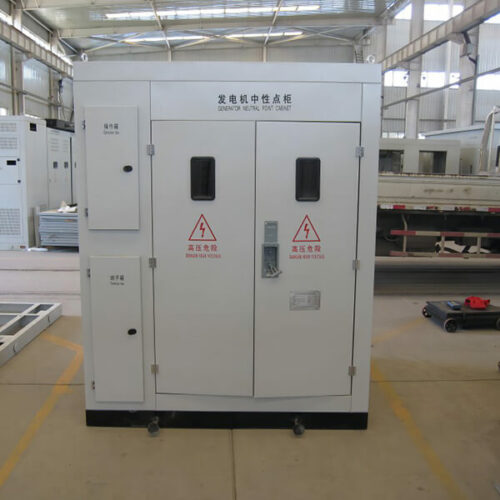
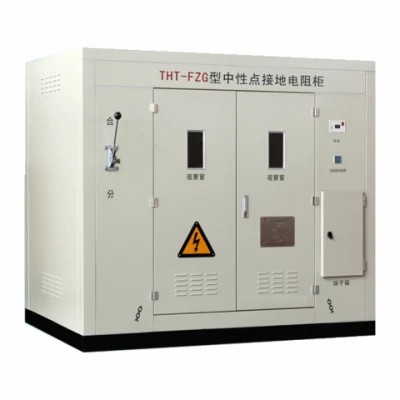
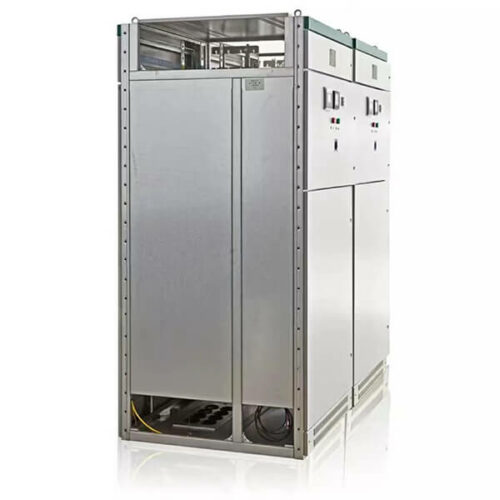
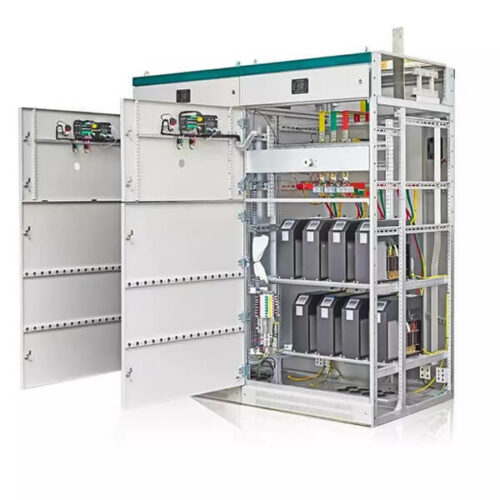
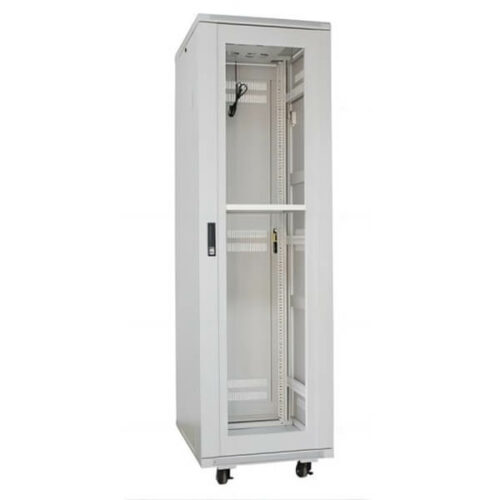
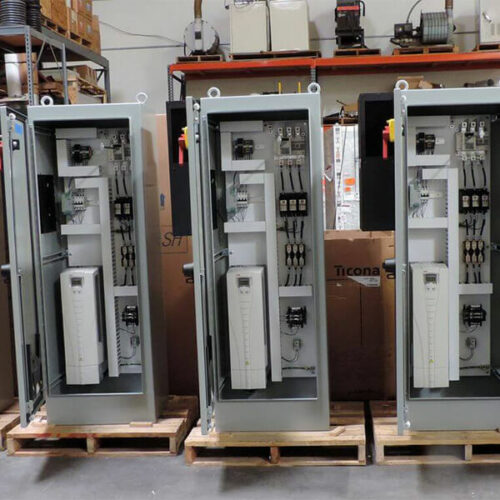
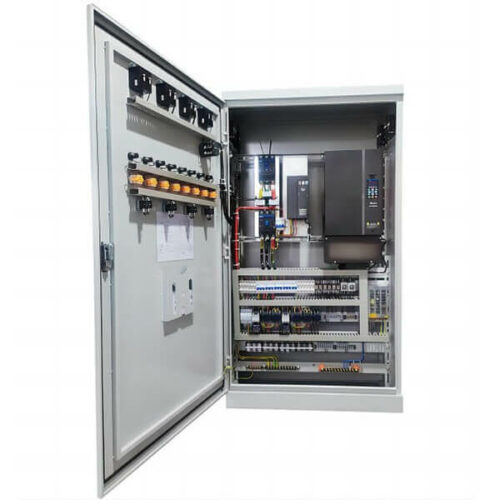
Metering cabinet is an essential component of switchgear, used to measure and monitor various electrical parameters, such as voltage, current, power, energy, and frequency, in power distribution systems.
Our metering cabinet is designed to meet the industry’s highest standards for accuracy, reliability, and safety. It comes with advanced features, such as digital display, data logging, communication interfaces, and protective functions, to provide real-time information and control over the electrical network.